Home > southern Home plansSouthern Home Plans
The design of southern home plans encompasses a range of features that contribute to their distinctive and charming aesthetic. Here are some key design elements commonly found in southern home plans:
1. Spacious Porches:
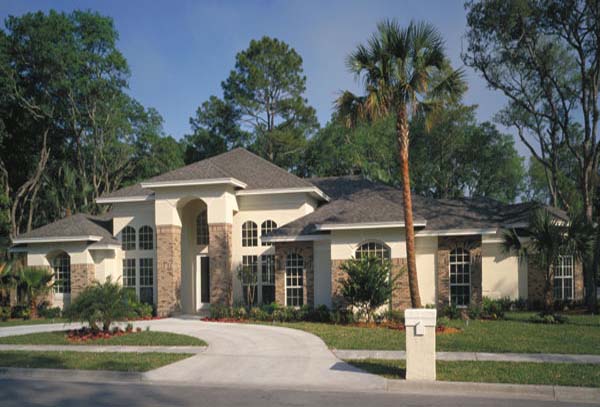
Southern home plans often feature expansive front porches that wrap around the front or sides of the house. These porches provide a welcoming space for relaxing, socializing, and enjoying the outdoors. They are typically large enough to accommodate seating areas, rocking chairs, and even outdoor dining spaces.
2. Functional Layout:
Southern homes often have a functional layout that prioritizes flow and convenience. Common features include an open floor plan, with the kitchen, dining, and living areas seamlessly connected. This design allows for easy movement and encourages a sense of togetherness among family members and guests.
3. Formal and Informal Spaces:
Southern home plans often include a mix of formal and informal spaces. Formal areas such as a dining room or a study may be designed with more refined architectural details and finishes. Informal spaces, such as a family room or a breakfast nook, are typically more relaxed and comfortable, reflecting the laid-back southern lifestyle.
4. High Ceilings:
Southern homes often have high ceilings, which create a sense of spaciousness and grandeur. Tall ceilings not only enhance the visual appeal of the interior but also help with ventilation and temperature regulation.
5. Deep Eaves and Overhangs:
The design of southern home plans often incorporates deep eaves and overhangs. These architectural features provide shade and protection from the sun, keeping the interior cooler and reducing energy costs.
6. Architectural Details:
Southern home plans pay attention to architectural details that add character and visual interest. These may include decorative moldings, columns, and trim work. Exterior details such as shutters, dormers, and gables enhance the overall charm and curb appeal of the home.
7. Natural Materials:
Southern homes often feature natural materials such as wood, brick, and stone. These materials contribute to the warm and inviting aesthetic and blend harmoniously with the surrounding environment.
8. Ample Windows:
Southern home plans incorporate generous windows to maximize natural light and provide views of the outdoors. Large windows allow for ample daylight, creating bright and airy interiors while also establishing a connection with the surrounding landscape.
9. Symmetry and Proportion:
Southern home plans often exhibit a sense of symmetry and proportion in their design. Balanced facades, evenly spaced windows, and a central entrance contribute to the overall harmony and elegance of the home's exterior.
10. Outdoor Living Spaces:
Southern homes embrace outdoor living with the inclusion of outdoor spaces such as patios, decks, and gardens. These areas serve as extensions of the indoor living spaces, providing opportunities for outdoor entertaining, relaxation, and enjoyment of the pleasant southern climate.
The design of southern home plans combines classic architectural elements, functional layouts, and an emphasis on indoor-outdoor living. The result is a timeless and inviting aesthetic that captures the essence of the southern lifestyle.• Five Regional Districts in southern Home
In the context of southern home design, there are several regional districts that are known for their specific architectural styles and influences. Here are five prominent regional districts in the southern United States, each with its own distinctive characteristics:
1. Lowcountry:
The Lowcountry region, encompassing areas of South Carolina and Georgia, is known for its unique architectural style influenced by English and Caribbean design elements. Lowcountry homes often feature elevated foundations, large wrap-around porches, shuttered windows, and plantation-style details such as columns and balustrades. The design is influenced by the region's hot and humid climate, with an emphasis on natural ventilation and outdoor living spaces.
2. French Creole:
The French Creole architectural style is prevalent in Louisiana, particularly in cities like New Orleans. This style is characterized by a blend of French, Spanish, and Caribbean influences. French Creole homes often feature a raised living area, known as a "gallery," which opens onto a courtyard. They typically have a symmetrical layout, steep roofs, wrought-iron balconies, and decorative details such as intricate woodwork and vibrant colors.
3. Southern Colonial:
The Southern Colonial style emerged during the colonial period in the southern states, including Virginia, North Carolina, and South Carolina. These homes often exhibit a symmetrical façade with a central entrance and evenly spaced windows. They feature two or three stories, with a large central hallway known as a "dogtrot" that provides ventilation and connects the rooms. Southern Colonial homes typically have simple and elegant exteriors, with elements such as brick or clapboard siding, gable roofs, and prominent chimneys.
4. Greek Revival:
The Greek Revival style became popular in the antebellum period and is characterized by its inspiration from classical Greek architecture. This style is prevalent in states such as Alabama, Mississippi, and Tennessee. Greek Revival homes feature symmetrical facades, grand entrance porticos supported by columns, and pediments above windows and doors. The design often includes stucco or brick exteriors, high ceilings, and formal interior spaces.
5. Texas Hill Country:
The Texas Hill Country region has its own distinct architectural style, influenced by German and European settlers in the area. Homes in this region often exhibit a blend of rustic and farmhouse elements. They feature limestone or stucco exteriors, exposed wood beams, metal roofs, and large covered porches. The design emphasizes a connection to the surrounding landscape, with expansive windows and open floor plans that integrate indoor and outdoor living spaces.
These regional districts represent just a few of the many diverse architectural styles found in southern home design. Each district showcases unique features and influences that reflect the history, culture, and climate of the respective regions, contributing to the rich architectural tapestry of the southern United States.
• Bat House in Southern Areas
A bat house in the southern area is a specialized structure designed to provide shelter and roosting opportunities for bats. Bats play a crucial role in the ecosystem by consuming vast numbers of insects, including agricultural pests, making them valuable for natural pest control. In the southern region, where warm climates are prevalent, bats are especially active and abundant.
A bat house in the southern area typically follows specific design guidelines to create an ideal habitat for bats. Here are some key considerations:
1. Placement: The bat house should be installed in a location that receives ample sunlight and is positioned at least 12-15 feet above the ground. It should be situated near a water source, such as a pond or stream, as bats require access to water for drinking and hunting insects.
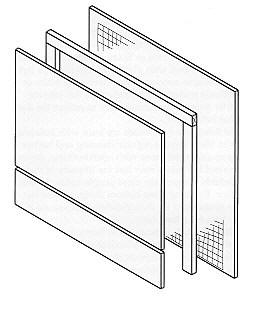
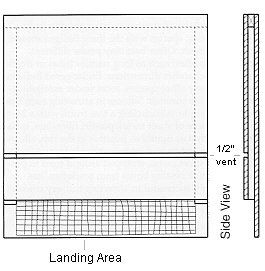
2. Size and Design: The size and design of the bat house should accommodate the species of bats commonly found in the area. Different species have varying preferences for roosting spaces. The house should include multiple chambers with appropriate dimensions and ventilation to accommodate different bat colonies.
3. Material: Bat houses are typically constructed using untreated wood, such as cedar or plywood, as it provides a suitable surface for bats to cling onto. The interior surfaces of the bat house should be roughened or grooved to facilitate bat roosting.
4. Entrance and Landing Area: The bat house should have a wide, open-bottomed entrance to allow bats to enter and exit easily. An extended landing area or porch below the entrance helps bats with their flight patterns and provides a space for them to hang.
5. Protection: The bat house should be designed to protect bats from predators, extreme weather conditions, and disturbances. It should have a secure structure, durable construction, and adequate insulation to regulate temperature and protect against heat or cold.
By providing a suitable habitat, bat houses in the southern area help promote the conservation of bats, support local ecosystems, and assist in natural pest control. They offer an alternative roosting option for bats, especially in areas where natural habitats such as trees or caves may be scarce or disrupted. Building and installing bat houses in the southern area can contribute to the preservation of bat populations and their ecological benefits.
• Procedure for constructing Bat House
Constructing a bat house for your southern home requires careful planning and consideration to provide an ideal habitat for bats. Here's a general procedure to follow:
1. Research and Design:
• Research local bat species and their preferences for roosting habitats.
• Choose an appropriate bat house design based on the species you want to attract.
• Consider factors like size, materials, and design features suitable for your region.
2. Gather Materials and Tools:
• Acquire the necessary materials, such as untreated wood (e.g., cedar or plywood), screws, and waterproof sealant.
• Gather tools like a saw, drill, screwdriver, measuring tape, and sandpaper.
3. Prepare the Wood:
• Cut the wood into appropriate dimensions according to your chosen bat house design.
• Roughen or groove the interior surfaces of the wood to provide bats with gripping surfaces.
4. Assemble the Bat House:
• Follow your chosen design plan to assemble the bat house using the prepared wood pieces.
• Secure the components together with screws, ensuring the structure is sturdy.
5. Create the Entrance and Landing Area:
• Cut a wide, open-bottomed entrance at the bottom of the front panel.
• Attach an extended landing area or porch beneath the entrance to aid bats in landing and takeoff.
6. Add Ventilation and Insulation:
• Create small ventilation holes or gaps near the top of the bat house to allow airflow.
• Insulate the bat house by adding a layer of natural, non-toxic insulation material inside.
7. Apply Waterproof Sealant:
• Apply a waterproof sealant to protect the wood from moisture and extend the life of the bat house.
• Ensure the sealant is completely dry and non-toxic before proceeding.
8. Install the Bat House:
• Determine the optimal location for the bat house on your southern property.
• Mount the bat house at least 12-15 feet high on a pole, building, or tree, ensuring it receives adequate sunlight and is away from direct human disturbance.
9. Monitor and Maintain:
• Regularly monitor the bat house for occupancy and maintenance needs.
• Check for signs of bat activity, such as guano or stains, to assess if bats are using the house.
• Clean the bat house annually to remove debris and maintain a healthy roosting environment.
Remember to research and comply with any local regulations or guidelines regarding bat conservation and the installation of bat houses. Providing a suitable bat house in your southern home can contribute to the conservation of bats, promote natural pest control, and enhance the biodiversity of your area.